Configuration
The SharePack is a SoftType that has the following data structure:
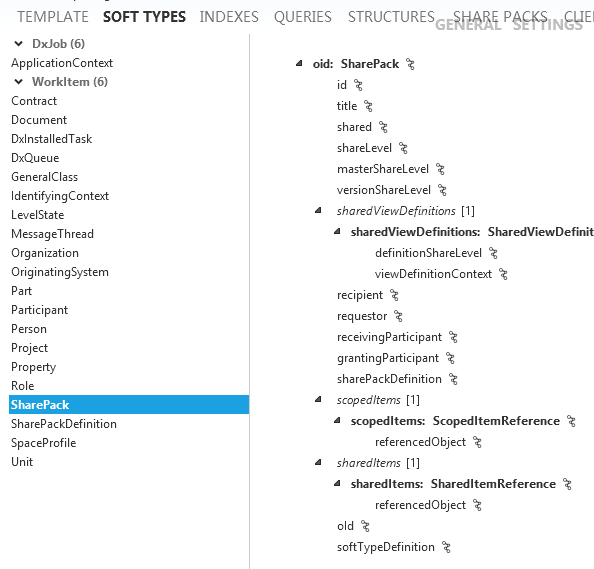
There are no "Views" in the SharePack SoftType but there are defaultIn and defaultOut schemas. Because there are no "Views" then the actual create/edit/read views are hard coded into ShareAspace.
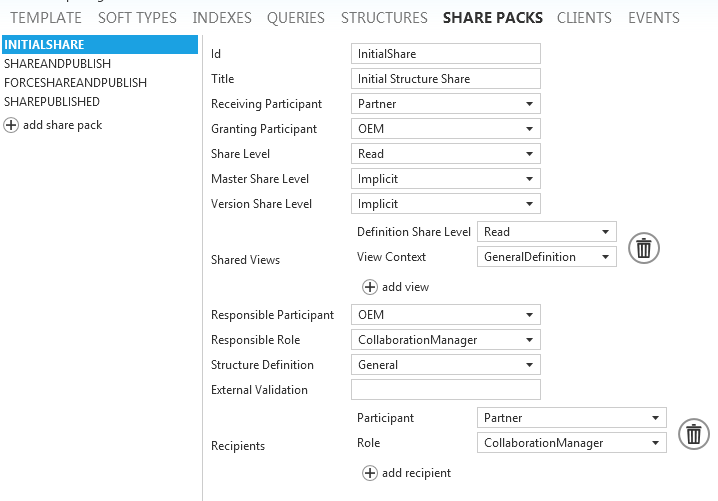
When you create a share pack definition in the "Share Packs" screen in the config tool, you see how this structure is used:
Then when you create an instance of this "SharePack" definition you can also see the same fields:
And in the Read view of the share pack instances you can also see all the SharePack Fields:
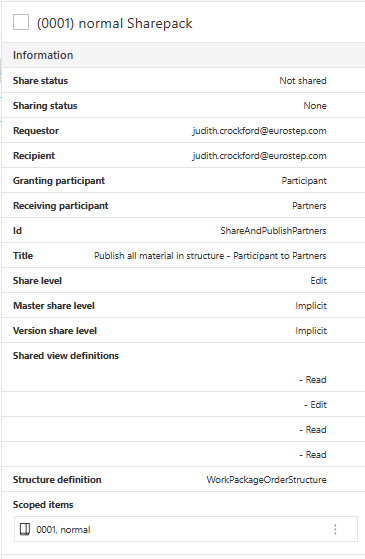
Share Package definitions
The sharePacks section of the Space Template is used for defining Share Package Definitions.
A Share Package has a title and a definition. It is possible to configure multiple Share
Package Definitions.
$receivingParticipantRef- reference to a$plmIdof a Participant in the Space Template. This Participant will be set to receive shared data from Share Packages using this definition$grantingParticipantRef- reference to a$plmIdof a Participant in the Space Template. This Participant will be able to use this definitionshareLevel- Read, Edit or None (see Share levels).masterShareLevel- Read, Edit or Implicit (see Share levels).versionShareLevel- Read, Edit or Implicit (see Share levels).resposible- an array of Roles in a Participant for which Users can approve a sharing request$participantRef- reference to a$plmIdof a Participant in the Space Template$roleRef- reference to a Role defined in the Space Template
recipients- an array of Roles in a Participant for which Users will receive a Work Item when data is shared with their Participant
"sharePacks": [
{
"id": "InitialShare",
"title": "Initial Structure Share",
"$receivingParticipantRef": "Partner",
"$grantingParticipantRef": "OEM",
"shareLevel": "Read",
"masterShareLevel": "Implicit",
"versionShareLevel": "Implicit",
"sharedViewDefinitions": [
{
"definitionShareLevel": "Read",
"$viewDefinitionContextRef": "GeneralDefinition"
}
],
"structureDefinition": "General",
"responsible": {
"$participantRef": "OEM",
"$roleRef": "CollectionOwner"
},
"recipients": [
{
"$participantRef": "Partner",
"$roleRef": "CollectionOwner"
}
]
}
]
Share levels
Share levels are used to control how to share the scoped items referenced by the share package, including any items found by walking the structure as defined in the referenced structure definition. Share levels are divided in to two sections, "Share level" that control the sharing of master only objects such as Unit, Classification and Change objects and master/version/definition share levels that control the sharing of master-version-definition objects such as Part and Document.
Tip
Read more about unit of information (UoI) and master-version-defintion (MVD) here:
Read more about shared access, ownership and history here:
Note
While it is possible to share reference data such as Unit and Classification it is recommended that common reference data is made available to all participants within a space to avoid repeated sharing the same information. To control the integrity of a share, the system tracks each share of an object, even when shared multiple times with the same participant. This can have an impact on performance. For example, if a Unit is not in a common area, and is used in 100 packages shared with another participant, the Unit is shared a 100 times. When one of those packages is unshared the system must maintain the share of the Unit because of the other 99 shares. The system cannot revoke access to the Unit until all 100 packages are unshared
shareLevel- control the sharing of master only objects explicitly referenced by the Share package or objects found while walking data according to a specifiedstructureDefinition.None- Master only objects are not shared.Read- The receiving participant is added as co-reader to the master only object, i.e. master object is shared with read access.Edit- The receiving participant is added as co-owner to the master only object, i.e. master object is shared with full access.
masterShareLevel/versionShareLevel/definitionShareLevel- control the sharing of master-version-definition (MVD) objects explicitly referenced by the Share package or objects found while walking data according to a specifiedstructureDefinition.masterShareLevelImplicit- if co-owner or co-reader is set on version or any definition within the unit-of-information (UOI) (i.e. contained within the master) the system will apply the default behavior and give read access to the master itself (excluding the non shared versions). e.g. if co-reader is set on a version someone reading the version needs to be aware of the identification of the master for the information to make sense.Read- The receiving participant is added as a co-reader of the master, granting read access to the whole UOI, i.e read access to the master, all its versions, and all definitions of all versions. If Edit access is specified on a lower level that edit access remains.Edit- The receiving participant is added as a co-owner of the master, granting full access to the whole UOI, i.e edit access to the master, all its versions, and all definitions of all versions. Including operations like creating new versions.
versionShareLevelImplicit- if co-owner or co-reader is set on any definition within the version the system will apply the default behavior and give read access to the version itself . e.g. if co-reader is set on a definition someone reading the definition needs to be aware of the identification of the version and the master for the information to make sense.Read- The receiving participant is added as a co-reader of the version, granting read access to the whole version, i.e read access to the version and all definitions of the version.Edit- The receiving participant is added as a co-owner of the version, granting full access to the whole version, i.e edit access to the version and all definitions of the version. This does not allow for the creation of versions.
definitionShareLevelNone- The definition is not shared.Read- The receiving participant is added as a co-reader of the definition, granting read access to the whole definition, i.e read access to all information on the definition.Edit- The receiving participant is added as a co-owner of the definition, granting full access to the whole definition, i.e edit access to all information on the definition.
Note
In practice for MVD objects:
- When using a definition centric approach where sharing is controlled on the definition level,
masterShareLevelandversionShareLevelwill always be set toImplicit. - When using a version centric approach where definition share levels are not set and
masterShareLevelis always set toImplicit. - When using a master centric approach where version share level and definition share levels are not set.
Runtime Share-pack definition
The following chapters explain how to create new share-pack definitions at runtime. New runtime share-pack definitions are needed when new participants are added at runtime to allow them to participate in the sharing of objects. It may be configured to do this automatically when a participant is added, but when this is not the case the following instructions may be used.
Template requirements
To be able to create share-packs in runtime the template must contain the following:
- Share-pack definitions. See Share Package Concepts and Share Package Definitions.
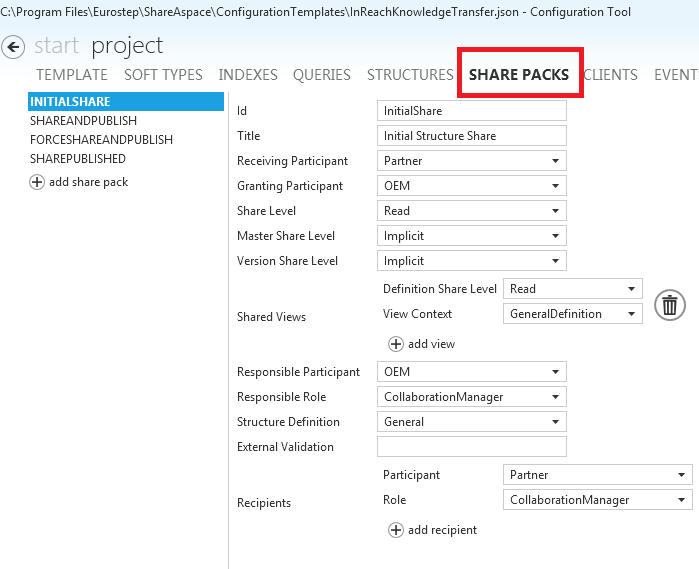
- "SharePack" module defined in the "Clients" section. This allows access to the runtime share-pack creation menus.
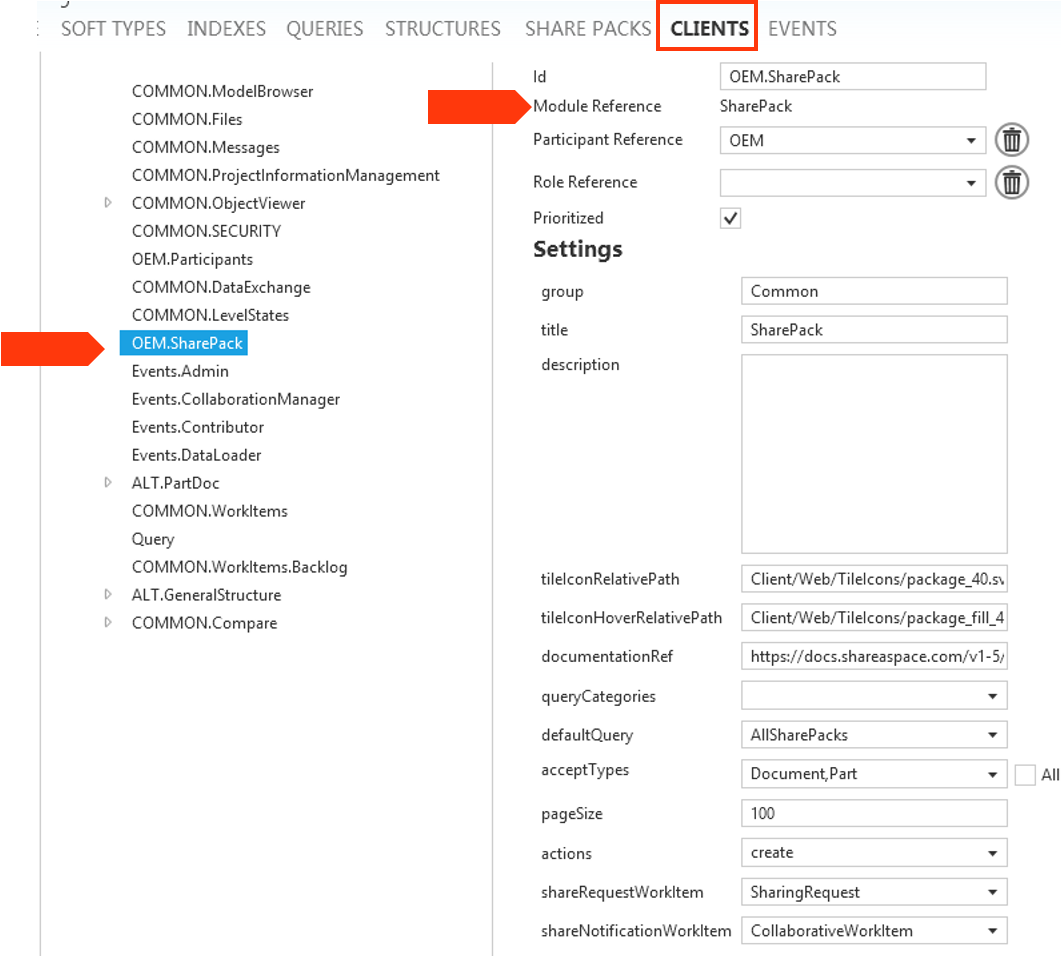
Runtime definition
Log into Nova with the user that has the rights defined in the templates "Client" section for the module "SharePack". You should then see a "SharePack" menu.
Log in as a user with a role permitted to access the "SharePack" module. The module is then visible in the user modules menu (see fix this https://docs.shareaspace.com/sas/introduction/user-interface.html#6-user-menu--modules-menu ) or as a tile (as shown below).
In the SharePack screen click on the "CopyDefinition" button.
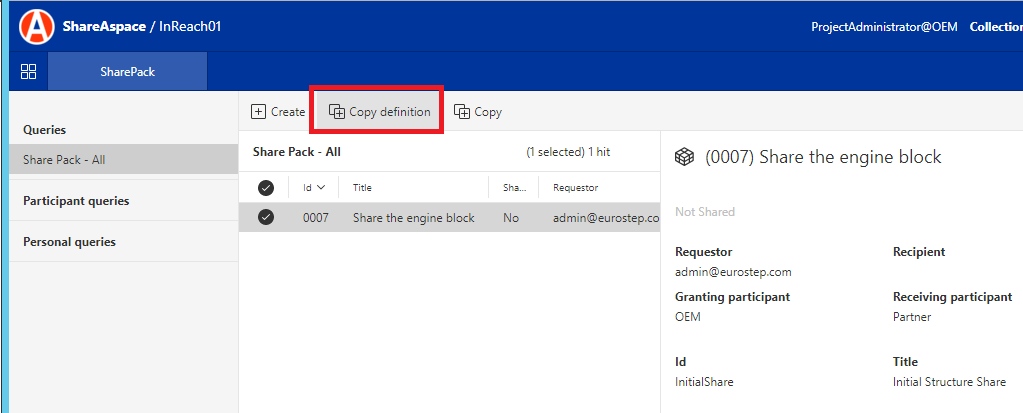
In the "Copy SharePack Definition" dialog select the "Share Package Definition" to be copied and complete the other required fields.
Note
If sharing extensions are used, they may have an expected Id naming convention.