Reference data
Introduction
Reference data refers to information that is commonly understood, agreed upon, and used consistently by all parties involved in a collaboration. It is typically defined before the collaboration begins, remains stable, and does not change throughout the process.
This type of data provides a shared vocabulary that ensures clarity and interoperability between systems, organizations, or teams.
Some examples of Reference Data are:
Unit of Measurement – Metre
All parties understand what a metre represents. Instead of redefining it, collaborators simply refer to it, ensuring consistency in measurements and communication.Information Classification – OFFICIAL-SENSITIVE (UK)
When a document is marked as OFFICIAL-SENSITIVE, all participants recognize the classification and its implications for handling, sharing, and security. This shared understanding avoids misinterpretation and ensures compliance.
In ShareAspace reference data is categorised as:
- Static Reference Data
- External Reference Data
- Dynamic Reference Data
Static Reference Data: Data that is always publicly available to all participants and users in a space. This is typically SoftTypes such as:
- GeneralClass,
- Property,
- Unit,
- Status.
- Countries
- Languages
The instances are established and agreed at the outset of a collaboration. They are intended to be stable for the lifecycle of a collaboration so will be static with occasional updates.
The data is loaded from a known set of master data sources under the governance of ShareAspace or the ShareAspace project team. Hence restrictions can be enforced to only receiving data from those master records.
External Reference Data: Data that is always publicly available to all participants and users in a space. These are SoftType instances that are created at runtime during a collaboration and are intended as a common point of reference for all participants in a space. The data is mastered in an external authoritative system. They include instances of:
- NATO Stock Items,
- Organizations,
- Geographical Locations, (not countries which are static)
Note that it is impractical to preload ShareAspace with External Reference Data due to the volume and the need to keep it up to date. (E.g there are at least 17M NATO Stock Items registered). Hence, External Reference Data is uploaded to ShareAspace on as needed basis. Furthermore, it can be uploaded to ShareAspace by different participants in a collaboration. For example, a supplier can provide a parts list with associated NSNs and manufacturers identified by CAGE codes. The NSNs and CAGE codes may not yet be loaded to ShareAspace.
Given that any participant can potentially upload External Reference Data a governance process is required to ensure the stability and quality of the data.
Dynamic Reference Data: Data that at given point in time is publicly available to all participants and users in a space. These are SoftType instances that are created at runtime during a collaboration and then a decision is made to provide them as a point of reference for all participants in a space. For example a set of company procedures could be made available to all participants and users in a space.
They include instances of:
- Standard Parts,
- Documents e.g. Collaboration procedures
- Projects,
Not all instances of the SoftTypes are necessarily reference data to be shared. The instance has to be explicitly identified to be a Dynamic Reference Data instance either by a user or by some criteria that automatically determines it. E.g a Part classified as a Standard Part is always treated as Dynamic Reference Data instance and is therefore available to all.
Dynamic Reference Data may not necessarily always be publicly available. E.g. a company procedure could be withdrawn.
Any user can create the data that will become Dynamic Reference Data, but typically it is only users in the specific roles that can designate data as Dynamic Reference Data. I.e. make it publicly available
The different types of reference data are summarized below:
| Characteristic | Static RD | External RD | Dynamic RD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Created when? | On space creation + runtime updates | Run time | Run time |
| Created by? | Template / Reference data manager | Any user | Any user |
| Administered by: | Static reference data manager | External reference data manager | Specified user role |
| Made public by? | On creation | On creation | specified user role |
| Governance / Data source | ShareAspace | External organizations | End users |
| Duration of availability | Always | Always | As needed |
| Stability | Does not change, apart from its status | Once verified, only changes to reflect changes in external system | Can be changed/versioned/retracted |
Standards based reference data
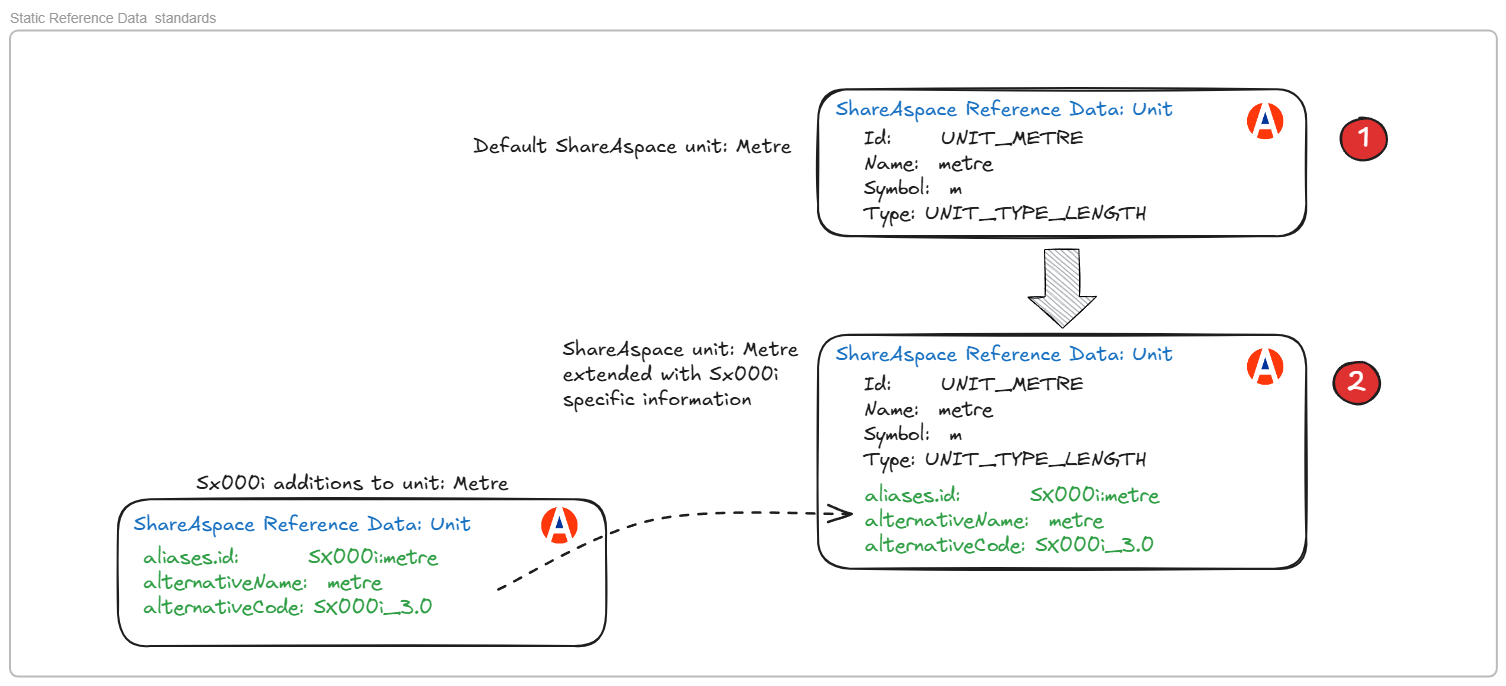
Static reference data is typically derived from standards. There may one definitive standard, other standards then provide alternative names or symbols and codes for the referenced data instance.
For example, a unit Metre is defined by the SI standard. It is also defined in the SX000i standards where the code MR is used in data exchanges.
Rather than having multiple instances of metre in ShareAspace for each standard, a single instance is created under the governance of ShareAspace. The codes, symbols etc from other standards are then added to / consolidated with the ShareAspace instance.
This is illustrated below.
Governance
Reference data needs to be trusted as accurate and up to date i.e. assured. Hence a number of features are implemented to ensure appropriate governance of the reference data.
Reference data management roles
Several user roles have been created explicitly for managing reference data to ensure adequate data governance of reference data. Namely:
StaticReferenceDataManager: The role for users managing Static reference data. Static reference data can only be created and updated by users in this role.ExternalReferenceDataManager: The role for users managing External reference data. Any user can create External reference data, however the data can only be changed by users in theExternalReferenceDataManagerrole.
Reference data accessibility
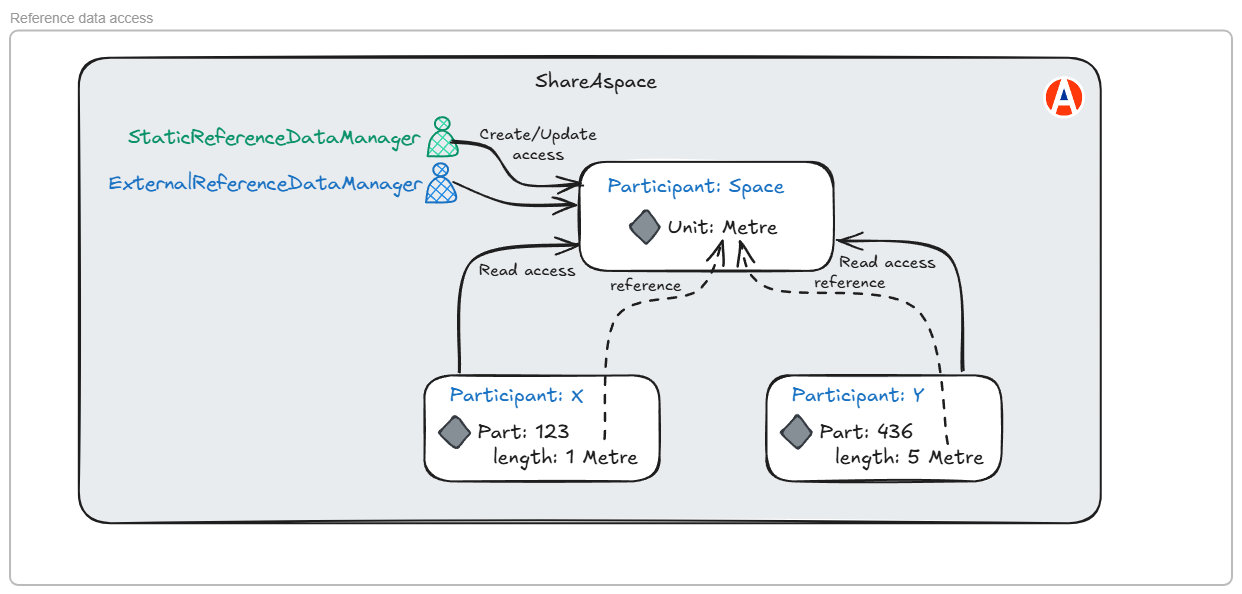
Reference data, by definition, needs to be accessible to all users in a collaboration space. Hence a Space participant is created explicitly in ShareAspace for the reference data. All reference data is owned by the Space participant and all Participants have read access to the Space participant.
The reference data owned by the space can only be updated by users granted a reference data governance role i.e. StaticReferenceDataManager and ExternalReferenceDataManager.
This is illustrated below.
External reference data accessibility.
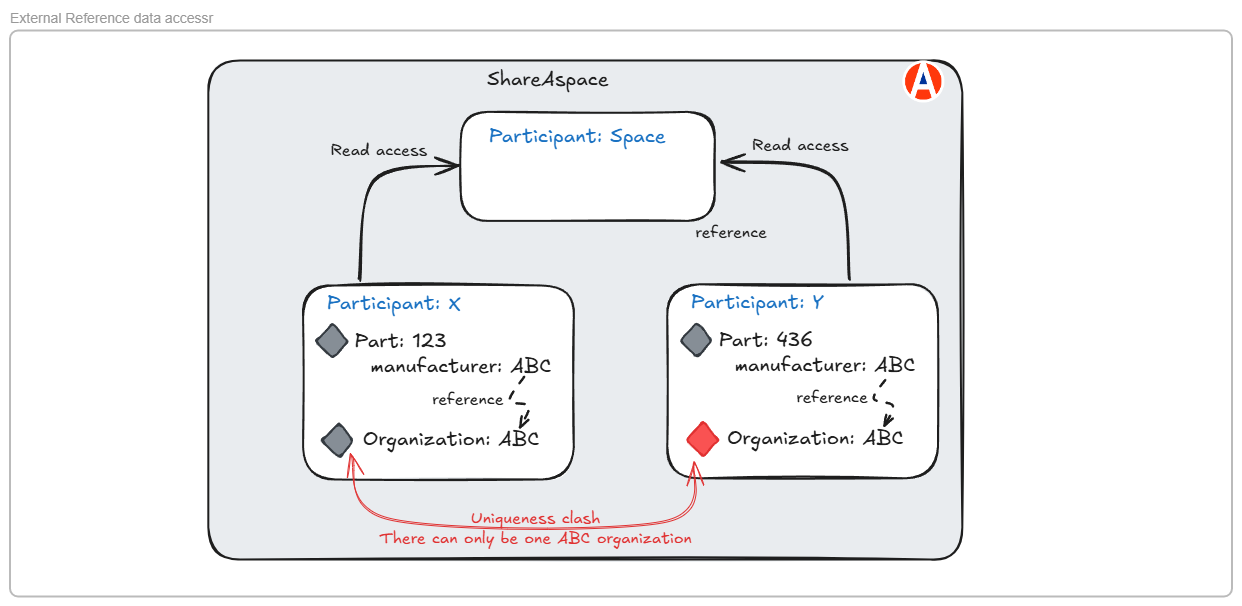
External reference data can be created by any user in any participant. A typical case where this occurs is where a supplier uploads data that includes references to reference data. For example, a parts list where each part references the part manufacturer. If the manufacturer organization does not exist in ShareAspace when the supplier imports the data, a new organization will be created. This organization will be owned by the supplier participant and therefore only visible to users who have a role in the supplier participant. This will cause uniqueness clashes if another supplier tries to import a file that references the same organization. This is illustrated below.
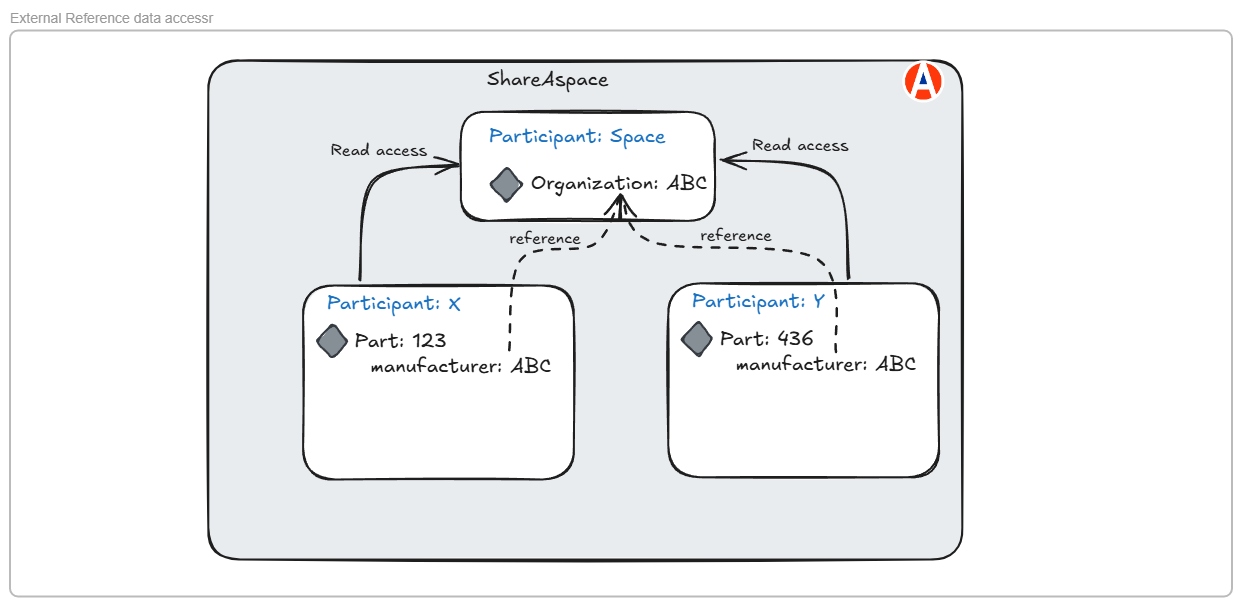
Consequently, the ownership of external reference data is transferred to the space participant as soon as it is created as shown below.
External reference data verification
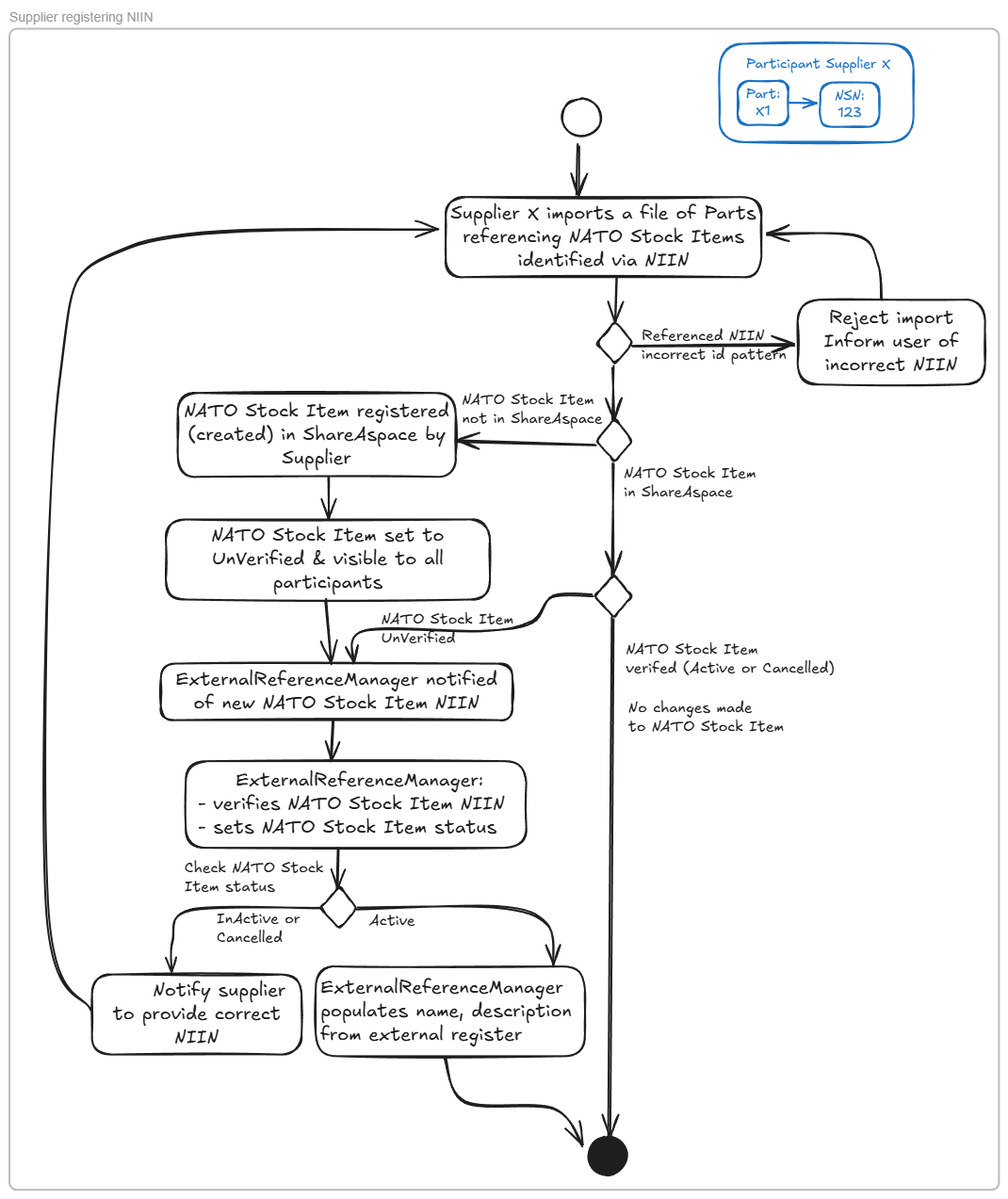
Reference data must be assured - that is trusted to be accurate and up to date. In the case of external reference data, users are referring to data that is mastered in external systems. For example Organizations are identified by CAGE codes and DUNS numbers which are created and manged by external organizations. Hence the external reference data should be checked for accuracy before it is used in ShareAspace. In particular that the CAGE code has been registered by the external organization and that its is identifying the same organization as has been loaded to ShareAspace.
Consequently a data quality process is implemented and the progress through the process is indicated by a status in the external referenced data as shown below:
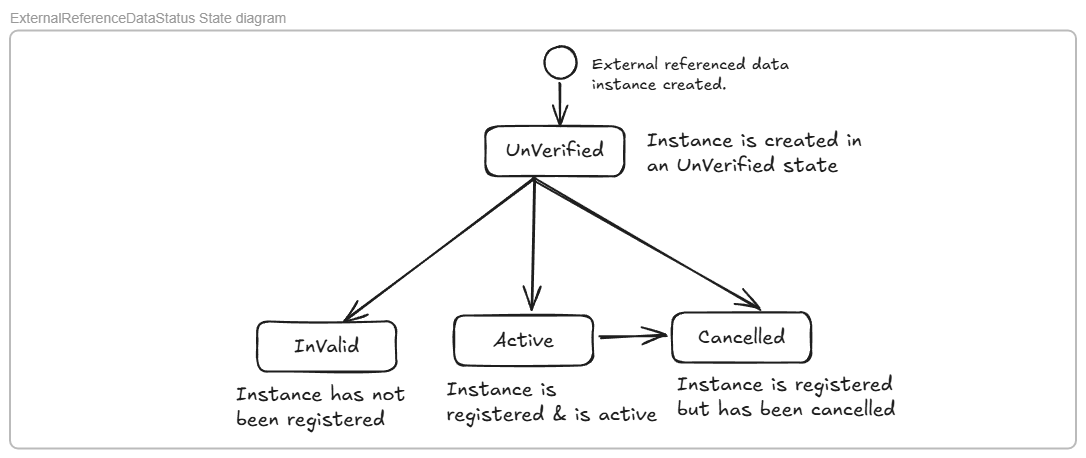
The example below shows the process for registering a NATO Stock item and verifying that the NSN is correct i.e. that it has been registered in a Codification Bureau of a NATO Member Nation.
Static reference data Origins / Master record
ShareAspace origins are used to ensure that static reference data is only intentionally created by the Static data manager and does not get inadvertently created by participants during file imports.
Hence there is an OriginatingSystem (origin) defined for importing Static reference data:
- SAsReferenceData:
sas:origin:referencedata
Any static reference data must be imported from the SAsReferenceData origin. Hence Static reference data is now imported by the reference data import jobs:
SoftTypeExcelReferenceDataImportJobSoftTypeJsonReferenceDataImportJob
These jobs have the origin context of the Static Reference Data set to SAsReferenceData sas:origin:referencedata
Packaged reference data
A set of referenced data is provided with ShareAspace for usage in deployments.
Reference data modules
The reference data is installed on the server at: C:\Program Files\Eurostep\ShareAspace\ReferenceData and is available as a set of referenced data modules that comprise of a set of Excel files that instantiate instances of reference data.
E.g.
C:\Program Files\Eurostep\ShareAspace\ReferenceData
ShareAspace.ReferenceData.PropertyAndUnit
UnitTypes.xlsx
MeasureValueTypes.xlsx
Properties.xlsx
PropertyTypes.xlsx
PropertyValueTypes.xlsx
Units.xlsx
ReferenceData.json
ShareAspace.ReferenceData.S-Series.SX000i.Unit.USCustomary
ReferenceData.json
SX000i_USCustomaryUnits.xlsx
ShareAspace.ReferenceData.Unit.SIBased.NamedDerived
NamedDerivedSIUnit.xlsx
ReferenceData.json
As described in Standards based reference data section, an instance of reference data can have additional information added to it from different standards. As it is not always appropriate to include all standards, there is an Excel file for core ShareAspace reference data, then Excel files for the information from standards that consolidates with the core ShareAspace reference data.
An example is shown below
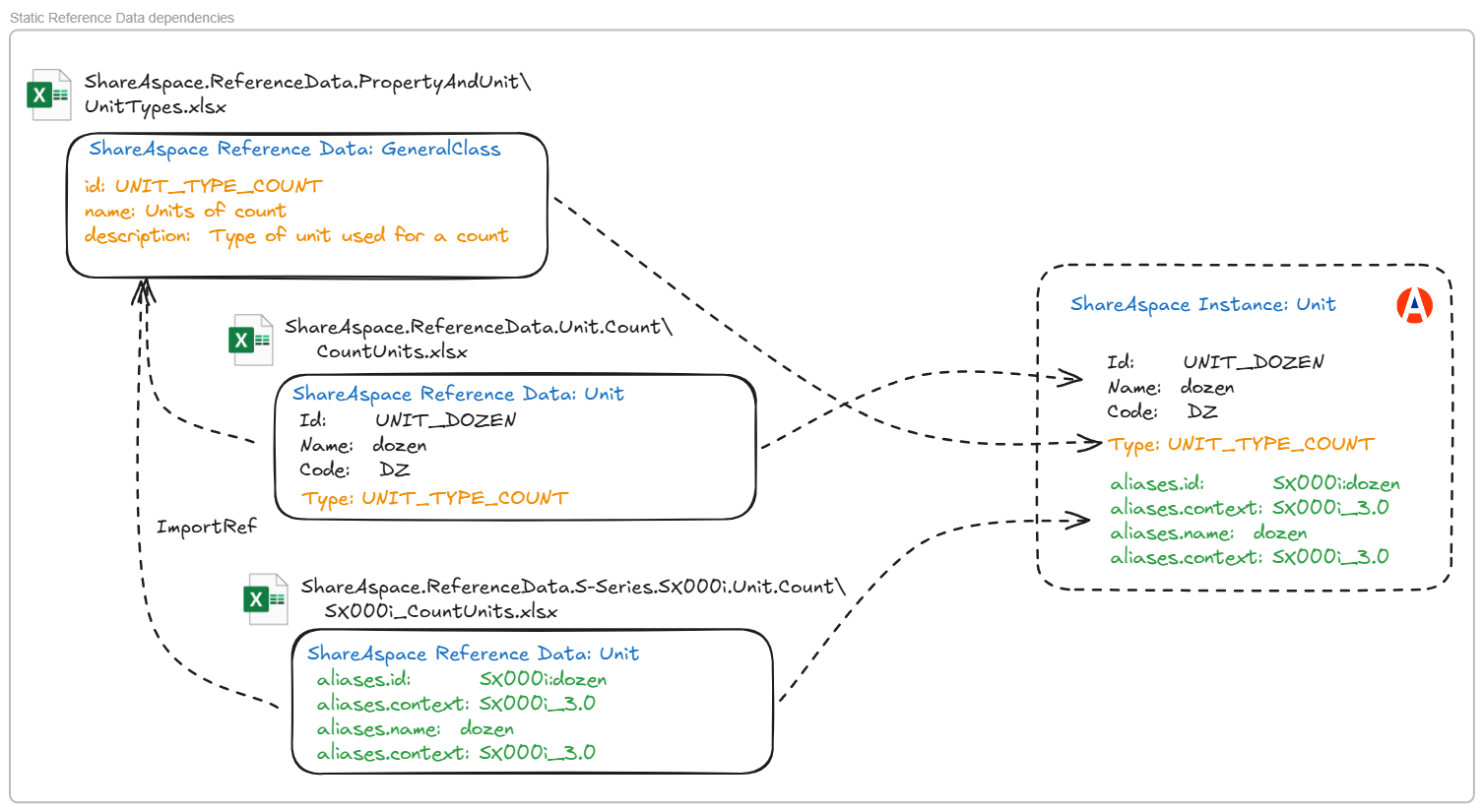
In the example shown, the Unit UNIT_DOZEN has the type UNIT_TYPE_COUNT.
The ShareAspace Unit: UNIT_DOZEN is defined in the file: ShareAspace.ReferenceData.Unit.Count\CountUnits.xlsx
The ShareAspace GeneralClass: UNIT_TYPE_COUNT is defined in the file: ShareAspace.ReferenceData.PropertyAndUnit\UnitTypes.xlsx
If the ASD reference data Sx000i is to be used then the Unit UNIT_DOZEN is extended by the file:
ShareAspace.ReferenceData.S-Series.SX000i.Unit.Count\SX000i_CountUnits.xlsx
The standards based Excel are effectively dependent on the core ShareAspace Excel. These dependencies are documented in a dependency file: ReferenceData.json
in a module. The file also indicates whether the reference data module is either:
- ShareAspace base reference data
- Standards based reference data that consolidates against the ShareAspace base reference data
- Project specific reference data that consolidates against the ShareAspace base reference data
- Project reference data that does not consolidate against the shareAspace base reference data
This is indicated by the "type" attribute which has the following allowed values:
ShareAspace- ShareAspace base reference dataStandardExtension- Standards based reference data that consolidates against the ShareAspace base reference dataProjectExtension- Project specific reference data that consolidates against the ShareAspace base reference dataProject- Project reference data that does not consolidate against the shareAspace base reference data
Note that the project reference data will not be maintained as part of the product
E.g.
ShareAspace-1.9\ShareAspace\CapabilityAssembler\ShareAspaceLibrary\src\ShareAspace.ReferenceData.PropertyAndUnit\ReferenceData.json
{
"module": "ShareAspace.ReferenceData.PropertyAndUnit",
"description": "Core properties, units and types",
"type": "ShareAspace",
"dependencies": []
}
ShareAspace-1.9\ShareAspace\CapabilityAssembler\ShareAspaceLibrary\src\ShareAspace.ReferenceData.Unit.Count\ReferenceData.json
{
"module": "ShareAspace.ReferenceData.Unit.SIBased.NamedDerived",
"description": "units that are derived from the seven base SI units and named for convenience",
"type": "ShareAspace",
"dependencies": [
"ShareAspace.ReferenceData.PropertyAndUnit"
]
}
Note that:
- the dependencies are at a module level. So if a dependent module contains multiple Excel files then the assumption is that a dependency refers to all of the Excel in that module. Furthermore, there is no need to specify the dependencies between the Excel files in the same module.
- the listed dependencies should only reference the immediate dependent module.
Reference data packages
The reference data modules can be grouped into packages and which can then be loaded / imported into a space.
The packages reflect a grouping of reference data relevant for a specific ShareAspace configuration e.g. D2M or IPS. They also are used to group the reference data according to the use of standards. E.g.
D2M SID2M reference data based on SI unitsD2M ImperialD2M reference data based on Imperial units
The reference data packages have the following format:
{
"package": "ShareAspace reference data",
"path": "C:/Program Files/Eurostep/ShareAspace/ReferenceData",
"description": "Core package for reference data for ShareAspace",
"referenceDataModules": [
{
"module": "ShareAspace.ReferenceData.PropertyAndUnit"
},
{
"module": "ShareAspace.ReferenceData.Unit.SIBased.NamedDerived"
}
]
}
Each package should define a complete set of reference data. If a reference data module is dependent on another module, then that module should be included in the package.
In the example, ShareAspace.ReferenceData.Unit.SIBased.NamedDerived is dependent on ShareAspace.ReferenceData.PropertyAndUnit hence ShareAspace.ReferenceData.PropertyAndUnit is included in the package.
The reference data package json can be constructed from the reference data modules files: ReferenceData.json that is stored with each reference data module.
Each module references a reference data folder - a reference data package. All Excel files in the folder are imported. E.g. The module: ShareAspace.ReferenceData.PropertyAndUnit
will load:
C:\Program Files\Eurostep\ShareAspace\ShareAspaceReferenceData\ShareAspace.ReferenceData.PropertyAndUnit
UnitTypes.xlsx
MeasureValueTypes.xlsx
Properties.xlsx
PropertyTypes.xlsx
PropertyValueTypes.xlsx
Units.xlsx
If there is mandatory reference data that is required by the template, then that should either be included in the template or explicitly loaded by the server setup scripts.
Deprecation process
A set of Static Reference Data is published as part of a ShareAspace release. This reference data is intended to be stable and long-lasting. However, some change is inevitable over time. The standards on which the reference data is based may evolve and some of the reference data may be deprecated.
For example a security classification of Restricted, used to classify documents, could be replaced by a new classification Sensitive.
It would not be appropriate for the Restricted classification to be simply removed and all uses replaced by Sensitive. It may be relevant to know that a document was previously classified as Restricted and is now classified Sensitive. Hence when reference data is deprecated, it is announced in the ShareAspace release notes, separated from the main set of reference data into an Excel suffixed with .deprecated.
ShareAspace deployment with reference data
The introduction of Static and External Reference Data enables ShareAspace projects to improve the overall quality of data. Only agreed reference data can be used. Duplicate data due to misspellings or abbreviations can be avoided. E.g The unit man hour has an agreed symbol of man-hour references to MH, ManHour will be rejected.
The consequence of using reference data is that projects must consider the following:
Identify a Reference data steward, a person or function responsible for identifying, creating and maintaining reference data during the ShareAspace deployment. The reference data stewards should be invited to ShareAspace as users in the External Reference Data manager and Static Reference Data manager roles.
Agree the set of Static Reference Data that is to be used during the collaboration.
Ensure that all data exchange mapper and spreadsheets used to enter data to ShareAspace are aware of the agreed set of Static Reference Data.
Establish a process (see External reference data verification) for managing External Reference Data. A common data quality issue is where users enter incorrect NATO Stock Numbers (NSNs) and CAGE codes. The use of External Reference Data enables data quality processes to be established under the governance of the reference data stewards, in this case the External Reference Data manager.
Considerations for ShareAspace 1.8 deployments
The use of reference data can be more controlled in ShareAspace 1.9 which will potentially impact on existing ShareAspace deployments. If the new approach is to be adopted on existing deployments there are a number of actions that need consideration.
If the new approach to managing Static Reference Data is adopted, the project should:
- Analyse what Static Reference Data is instantiated and what is actually required.
- Should it be public. I.e is any of the Static Reference Data currently owned by a participant? If so should the ownership be transferred to the space participant?
- Was it intentionally created by the participant as private reference data or was it created erroneously?
- Develop a plan to migrate the existing Static Reference Data
- Check the existing approaches to inputting data to ShareAspace.
- Are the importers free to create any reference data? e.g do you just import a file of parts with new properties and units? If so, this will potentially create new instances of units and properties in ShareAspace. Is this intentional?
- Develop a plan to update the importers to handle origins on Static Reference Data
- Develop a plan to update the ShareAspace template.
If the new approach to managing External Reference Data is adopted, the project should:
- Be aware that External Reference Data can be created by any user, but the ownership will then transfer to the Space participant. Hence only External Reference Data managers will be able to edit External Reference Data once it has been loaded
- Develop a process for managing the quality of External Reference Data.
- Analyse what External Reference Data has been instantiated and which participant owns it.
- Should the External Reference Data e.g. Organization be public?
- Was it intentionally created by the participant as private reference data or was it created erroneously?
- Develop a plan to migrate the existing External Reference Data
- Develop a plan to update the ShareAspace template.
Limitations
Currently Static reference data can only be updated via file import. It is not possible to edit the data directly from the user interface.